Disaster Recovery 101 — The Beginner’s Guide
We live in a digital world where data is a critical
constituent for business success.
But bad things happen to good data.
Disaster is real and may cause harm to any
business of any size and any segment. There are so many related concepts and
terms and it is becoming vital to understand these terms to ensure data availability.
If you were looking for a guide on what is business
continuity, disaster recovery and other associated terms — you are in the right
place. Understanding the disaster recovery can be tricky, but it’s never too
late to learn the basics: make yourself comfortable, we are about to start with
the nuts and bolts!
What is disaster recovery?
Disaster recovery (DR) is a set of procedures which must be taken due to an unplanned
event (disaster) that disrupts the company’s resources and puts day-to-day
processes and operations at risk. Disaster may come in all forms and sizes and
may happen due to multiple reasons: natural disasters, hardware failures, human
errors or cybercrimes. The number of potential threats to your company is
infinite: from an accidental fire (electrical equipment and appliances may be
caused by things such as plugs, cables, etc.) to full-blown natural disasters
and power outages (e.g. thunderstorm, flood, etc.)
The goal of DR is to keep the company’s
operations as close to “business as usual” as possible.
Disaster recovery vs business continuity — Understanding
the difference
When talking about disaster recovery and business
continuity it can be easy to fall under the impression that these terms
represent the same thing. Well, is there actually a difference?
The short answer — yes, there is!
Even though business continuity and disaster
recovery are firmly connected in your data protection strategy, there are
distinctions between these two concepts. Here are the differences:
Disaster recovery revives the company’s operations and processes once disaster
strikes, it IS about bringing things back (e.g. applications) — this is how you
respond to a disruptive event.
Business continuity is focused on mission-critical
services that your business needs in order to properly function. It IS about
services and putting users back to work.
Imagine that you’re using Microsoft’s
communications tool, the Microsoft Teams app, for instant messaging within your
organization. Disaster happened. Due to a power outage and API errors, all
servers are down and unavailable.
To give you an illustration of what that means if we talk DR and BC definitions — look at the table below:
Disaster recovery is a part of business continuity
planning, thus the two expressions are used as BCDR
in industry. Together they answer, “What if (put the worst scenario here)
happens?” question and both determine what the next steps are that need to be
taken to keep your business afloat.
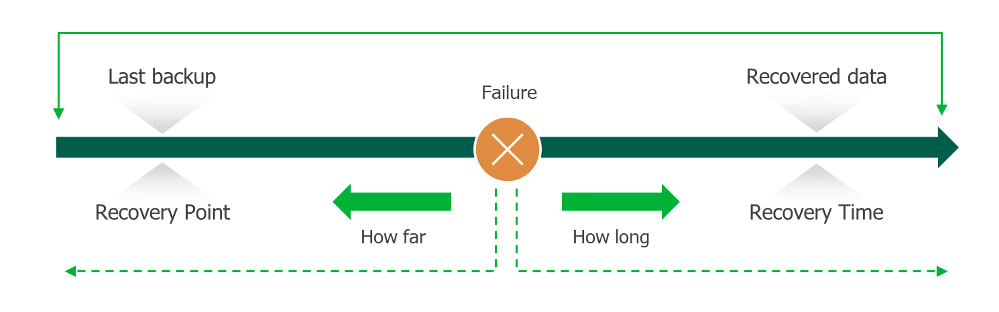
RTO and RPO — Key metrics of business continuity
Recovery Time
Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) are two core parameters that
enterprises consider when maintaining business continuity.
Recovery Time
Objective (RTO) is a time,
within which all operations must be back to normal after disaster strikes.
Recovery Point
Objective (RPO) is
a maximum period (measured in
minutes and hours) on which data and
operations can be lost between the last backup and the disruptive event. RPO is
set by the business continuity plan.
RTO and RPO metrics can differ from company to company but should be defined with a business priority to ensure data availability — this can depend on several factors from an organization’s size to its business type, structure, existing in-house resources and other parameters.
Disaster recovery planning components
Dozens of fires flared up in Australia in
late 2019. Consulting company SGS Economics estimated up to $50 million (AUD) a day in disruption. These
costs relate to different matters, such as employees missing work because of
health issues or insurance losses, as well as costs associated with data corruption
and the absence of a disaster recovery plan and its testing.
It’s difficult to believe that some
companies still don’t have a disaster recovery plan in place. But why it is so
hard to get it implemented? What are the key elements of a DR plan? Let’s sort
this out:
1. Know your applications and hardware
Document information about every piece of software and hardware you
have, keep it up to date and make sure you have technical support details for
each item.
2. Define your RTO and RPO parameters
Assess what is an acceptable recovery time for each business
function, as well as every program, operating system, server and storage device
to get back up: First — applications, second — services.
3. Determine the SLAs for an outsourced DR solution
Ensure that you have documented service level agreements (SLAs) with
an outsourced vendor in the case of a disaster.
4. Document a data backup plan
What happens to your data if disaster strikes? How many copies are
being created? Are they stored off site? These and other questions must be
defined in your backup plan.
5. Compliance — Make sure you’re compliant
It’s the company’s responsibility to ensure reliability and availability
of its data. Non-compliance is not an option and can lead to both reputational and
financial risks.
6. Define roles and responsibilities within your staff in the
case of a disruptive event
Assign roles to members of your organization and make sure it’s well
communicated: there should be a specified plan of action in the case of a
disaster event.
7. Create an emergency communication plan
Document how you communicate with people, whether it’s your
customers or employees, until business operations are back to normal.
8. Again and again test your DR plan
Having a disaster recovery plan isn’t enough. If you don’t test your
plan — you can’t rely on it, therefore disaster recovery testing is a
difference maker here. Regular, full-scale testing is a must to the success of
a rigorous disaster recovery plan, especially for multi-site environments. Once
you have a DR plan in place — make sure you test it frequently and thoroughly.
Alternatives? Disaster Recovery as a Service
Gartner estimates that businesses will have invested more than $3.7 billion in the Disaster Recovery as a Service market
through 2021. From small businesses to
immense corporations, organizations are adopting cloud technologies at a rapid
pace. This is clearly a trend that looks set to continue. But before going any
further, let’s quickly define the basic terms of cloud disaster recovery.
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) is an outsourced (hosted by a third party vendor)
cloud-based model, which is essentially a replication of physical and virtual
servers. DRaaS can be primarily useful to enterprises that lack the required
expertise to build and test an efficient disaster recovery plan.
Undoubtedly, there are certain benefits of DRaaS,
such as:
- Affordable cost — DRaaS is pay-as-you-use managed service. Use of off-site storage also leads to meaningful savings in storage and software needs
- Accessibility — You’ll be able to access your system from any location. All you need is an internet connection
- Ease of use — You will get full expert support from a service provider to handle unexpected events, efficiently and quickly
While enterprises embrace a multi-cloud world,
whether in addition to or separate from an overall data protection strategy —
choosing a right DRaaS solution can be challenging.
Here’s how Veeam solves disaster recovery, orchestration
and automation challenges
At the age of Digital Transformation business
continuity should be a priority for companies and Veeam can help you in
addressing these challenges listed above — whether you’re looking for a DRaaS
solution or if you would like to improve your DR processes and migration while maintaining
service continuity.
Veeam defines DRaaS by offering it as part
of a comprehensive availability strategy, providing a consistent user
experience and reducing the overall cost to protect your data. If you want to
learn more on how to get affordable, efficient, imaged-based replication for
true DR — please check out this page.
What about intelligent orchestration for DR? Veeam offers Veeam Availability Orchestrator, a solution that delivers reliable, scalable and easy-to-use orchestration and automation, allowing DR failover and restore plan creation, documentation, testing and execution in VMware vSphere environments.
Feel free to check out the Veeam
Availability Orchestrator user guide to learn
more about its features or you can go ahead and download a free trial now.
May your data stay safe!
The post Disaster Recovery 101 — The Beginner’s Guide appeared first on Veeam Software Official Blog.
Veeam
via Veeam Software Official Blog https://ift.tt/21VeTDG
March 30, 2020 at 04:25PM
Kseniya Skovorodko
